- June 25, 2024
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has published Cabinet Decision No. (49) of 2021, which amends Cabinet Decision No. (40) of 2017 on Administrative Penalties for Violations of Tax Law in the UAE. The amendments have came in effect since 28 June 2021.
After the amendments, VAT penalties and fines in UAE have been reduced substantially as compared to the previous legislation.
This article compares the penalties that were applicable previously and the new penalties.
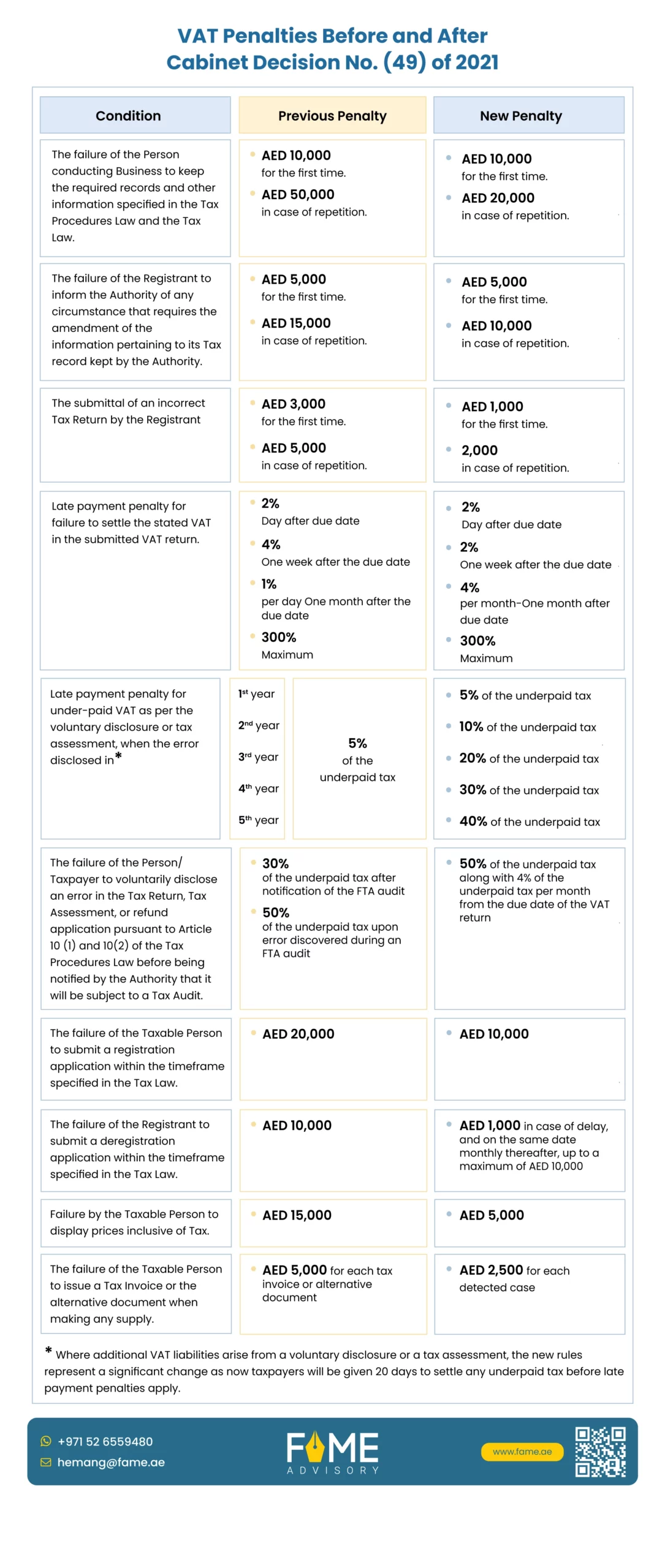
Below is the comparison between the penalties that were applicable previously and the new penalties.
VAT Penalties and Fines in UAE: Before and after Cabinet Decision No. (49)
Failure to keep required records and other information
The failure of the Person conducting Business to keep the required records and other information specified in the Tax Procedures Law and the Tax Law. Before the amendment, the previous penalty imposed was AED 10000 for the default that happened the first time, and in case of repetition, it would be AED 50,000. After the amendment, the penalty in case of default repeats changed and was reduced to AED 20,000.
For example, in case if a business does not maintain invoices and receipts for sales made in January and June during the year 2024, it would be penalised with AED 10,000 for the first default in January and AED 20,000 for the repetitive default that happened in June.
Failure to inform the Authority of the amendment of tax record information
The failure of the Registrant to inform the Authority of any circumstance that requires the amendment of the information pertaining to its Tax record kept by the Authority. The previous penalty was AED 5,000 for the first time and AED 15,000 in case of repetition. However, in the case of the repetition of default, the penalty has decreased to AED.
For example, a company that moves to a new address but does not inform the tax authority about the change in its official records in 2023 and further changes its shareholders in 2023 would be penalised AED 5,000 for the default of address change in 2023 and AED 10,000 for the default in updating the shareholders' records.
Submittal of an incorrect Tax Return by the Registrant
The penalty for the submittal of an incorrect Tax Return by the Registrant was AED 3,000 for the first time and AED 5,000 in case of repetition. This has now changed to AED 1000 in the case of the first default and AED 2000 in the case of repetitive default.
For example, if a company submits a VAT return showing fewer sales than the actual need, it will be penalised AED 1,000 for the first default in 2023.
Late payment penalty for failure to settle the stated VAT in the submitted VAT return:
Late payment penalties for underpaid VAT as per the voluntary disclosure or tax assessment were 2%-Day after the due date, 4% one week after the due date, 1% per day one month after the due date, and which could go up to a maximum of 300%.
Now, the penalty is 2% a day after the due date, 2% one week after the due date, and 4% per month one month after the due date, which can go up to 300% maximum.
When a business has submitted its VAT return on time but fails to pay the due VAT amount of AED 50,000 by the deadline, it needs to pay 2% of the unpaid tax immediately, i.e. AED 1,000, plus 4% per month up to 300% of the unpaid tax, i.e. maximum up to AED 150,000.
Late payment penalty for underpaid VAT as per the voluntary disclosure or tax assessment
Where additional VAT liabilities arise from a voluntary disclosure or a tax assessment, the new rules represent a significant change. Now, taxpayers will be given 20 days to settle any underpaid tax before late payment penalties apply.
A company based on a voluntary disclosure finds that they owe an additional VAT of AED 20,000. They do not pay the amount within 20 days.
- Year 1: 5% of the underpaid tax (AED 1,000)
- Year 2: 10% of the underpaid tax (AED 2,000)
- Year 3: 20% of the underpaid tax (AED 4,000)
- Year 4: 30% of the underpaid tax (AED 6,000)
- Year 5 or thereafter: 40% of the underpaid tax (AED 8,000)
Failure of the Person/Taxpayer to voluntarily disclose an error
The failure of the Person/Taxpayer to voluntarily disclose an error in the Tax Return, Tax Assessment, or refund application pursuant to Article 10 (1) and 10(2) of the Tax Procedures Law before being notified by the Authority that it will be subject to a Tax Audit.
The previous penalty was 30% of the underpaid tax after notification of the FTA audit and 50% of the underpaid tax upon the error. The penalty is 50% of the underpaid tax, along with 4% of the underpaid tax per month from the due date of the VAT.
A taxpayer realises they made a mistake in their previous tax return but does not report it before receiving a notice of a tax audit, where the undeclared amount is AED 10,000. It needs to pay 50% of the undeclared tax amount, i.e. AED 5,000, along with 4% from the due date of the VAT return.
Failure of the Taxable Person to submit a registration application
The penalty for failure of the Taxable Person to submit a registration application within the timeframe specified in the Tax Law previously was AED 20,000, which is reduced to AED 10,000.
A business that reaches the turnover threshold for VAT registration but fails to apply for registration within the timeframe specified by the Tax Law needs to pay AED 10,000.
Failure of the Registrant to submit a deregistration application
In case the Registrant fails to submit a deregistration application within the timeframe specified in the Tax Law, the law previously imposed AED 10000. Now, the penalty is changed to AED 1,000 in case of delay, and on the same date monthly thereafter, up to a maximum of AED 10,000.
A company stops trading and is no longer required to be VAT registered but does not apply for deregistration in a timely manner and thus needs to pay AED 10,000.
Failure by the Taxable Person to display prices inclusive of Tax
If the Taxable Person fails to display prices inclusive of Tax, a penalty of AED 5000 will be imposed, which previously was AED 15000.
A businessman who advertises products with prices that do not include VAT, contrary to the requirement to display tax-inclusive prices, would need to pay AED 5,000 per instance.
Failure of the Taxable Person to issue a Tax Invoice
The failure of the Taxable Person to issue a Tax Invoice or the alternative document when making any supply earlier attracted a penalty of AED 5,000 for each tax invoice or alternative document, whereas now it is AED 2,500 for each detected case.
A service provider does not issue a tax invoice to its clients for services provided in the year 2024. He needs to pay AED 2,500 per invoice not issued.
Implications of the Amendments to VAT Penalties and Fines in UAE
Overall, after the amendments, the penalty has been reduced, and it has adopted a supportive approach towards business. By reducing VAT fines, the UAE tax authority aims to create a more business-friendly environment, reducing the financial burden and encouraging compliance. Below are the key changes:
- Ensure Compliance with the Law: The reduced penalties will encourage businesses to comply with tax without the fear of high penalties.
- Supporting Businesses: By reducing the fines, the TAX authority is giving its support to those who usually struggle with high penalties.
- Promoting Voluntary Disclosures: By giving the grace period for voluntary disclosures, the businessman will come forward and rectify errors early.
- Improving Record-Keeping and Reporting: The reduced penalties for record-keeping and reporting will encourage businesses to maintain correct and updated records.
- Increase Focus on Business Operations: By making the tax compliance process easy and smoother, businesses can focus on their growth and development.
Final Words on VAT Penalties and Fines in UAE
The amendments introduced through Cabinet Decision No. (49) of 2021 marks a significant shift VAT penalties and fines in UAE, now aiming to foster a more supportive environment for businesses. With such a reduction in penalties across various violations, the UAE tax authority seeks to encourage compliance and promote a culture of voluntary disclosure and accurate record-keeping.
Therefore, the new framework reflects a step towards enhancing business confidence and ensuring economic development in the UAE.
At FAME, we help businesses understand these changes and ensure that your business stays compliant with VAT regulations and minimises risks of fines and penalties. We guide businesses to overcome VAT compliance challenges and optimise their performance in the UAE market.





